Open Source Software Supply Chain
Understanding Open Source Software Supply Chain
The open source software supply chain refers to the intricate ecosystem of various components used to develop, distribute, and maintain open source software. This chain includes a variety of actors such as developers, maintainers, repositories, and end-users. Due to the collaborative nature of open source development, software often integrates code from multiple sources, making the supply chain both complex and expansive.
One of the primary benefits of open source software is the ability to reuse existing code, which accelerates development and increases innovation. However, this same characteristic introduces potential risks. For instance, vulnerabilities in widely-used open source libraries can propagate across numerous projects, posing significant security threats. These vulnerabilities can be introduced either unintentionally or maliciously, potentially affecting thousands of software applications that rely on the compromised component.
To mitigate these risks, various strategies and tools have been developed. Package managers like npm for JavaScript, pip for Python, and Maven for Java provide mechanisms to manage dependencies effectively. Additionally, automated tools such as Snyk, Black Duck, and Sonatype Nexus can scan for and alert on known vulnerabilities within a project's dependencies. These tools often provide actionable insights to resolve identified issues promptly.
Another critical element of the open source software supply chain is license compliance. Different open source projects come with various licenses (e.g., MIT, GPL, Apache), each stipulating how the software can be used, modified, and redistributed. Failure to comply with these licenses can result in legal complications. Tools like FOSSology and OpenChain help in ensuring that all license conditions are met, thereby reducing legal risks.
Collaboration and transparency are fundamental to the health of the open source supply chain. Communities often band together to audit code, share knowledge about best practices, and contribute patches or improvements. This collective effort not only enhances the quality of the software but also ensures a robust security posture. Moreover, major industry players have started initiatives such as the Open Source Security Foundation (OpenSSF) to further bolster supply chain security.
In conclusion, while the open source software supply chain offers substantial benefits in terms of innovation, cost, and speed, it also necessitates diligent management to address security and compliance risks. As the adoption of open source software continues to grow, so too will the need for advanced tools and strategies to ensure the integrity and reliability of the supply chain.
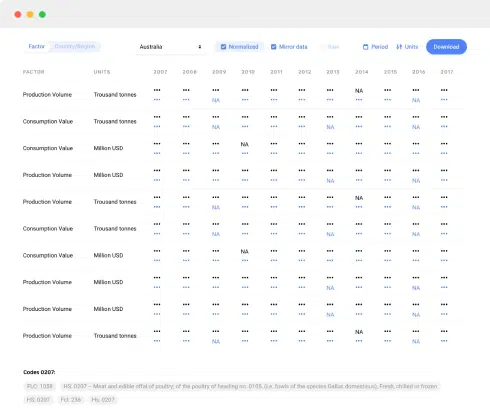
Nothing found. Please try again.
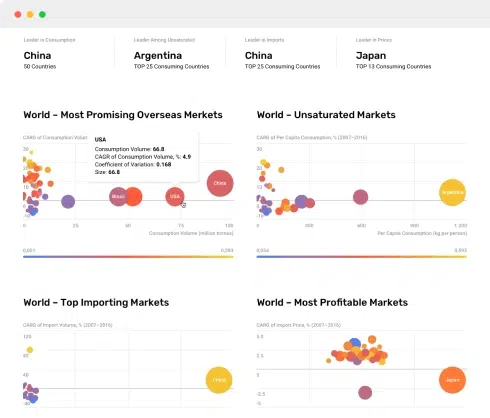
Nothing found. Please try again.
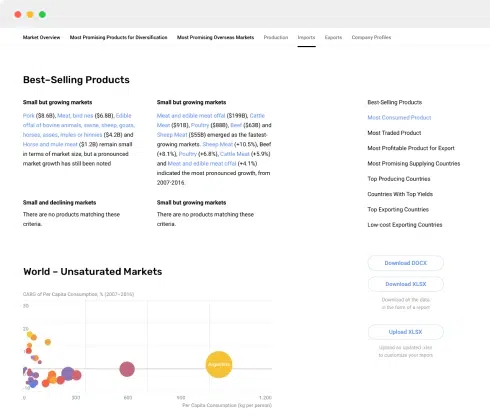
Nothing found. Please try again.