Supply Chain Systems and Tools
Supply chain systems and tools are critical components in managing the flow of goods, information, and finances as they move from supplier to manufacturer to wholesaler to retailer to consumer. These systems encompass a wide variety of tools that assist in different aspects of supply chain management (SCM). Below are key elements and tools used in supply chain systems:
1. Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) Systems: ERP systems integrate all facets of an enterprise into one comprehensive information system that can be accessed by individuals across an entire organization. They manage and configure complex supply chain processes, including procurement, manufacturing, logistics, warehousing, inventory, and order fulfillment.
2. Supply Chain Planning (SCP) Tools: These tools assist in forecasting future demands, planning material requirements, and scheduling production. SCP tools use algorithms and statistical models to predict product demand and optimize production schedules and inventory levels.
3. Transportation Management Systems (TMS): TMS aids in the planning and execution of the physical movement of goods. Functions of TMS include selecting the best transport routes, managing fuel costs, and optimizing freight costs.
4. Warehouse Management Systems (WMS): WMS deals with the optimization of warehouse operations, from receiving goods, inventory management, picking, packing, and shipping. It ensures warehouse activities are executed as efficiently as possible.
5. Supplier Relationship Management (SRM): SRM tools help organizations manage their interactions with third-party suppliers. They aid in selecting suppliers, negotiating contracts, and maintaining relationships.
6. Customer Relationship Management (CRM): CRM tools are used to manage a company's interactions with potential and current customers. In the context of SCM, they help in understanding customer needs and improving customer service.
7. Blockchain Technology: Blockchain can enhance supply chain transparency and traceability. It allows secure, transparent transactions, and can significantly reduce the risk of fraud.
8. Internet of Things (IoT): IoT devices can track and monitor goods in transit. Sensors can monitor conditions such as temperature and humidity, ensuring goods remain in optimal conditions.
9. Advanced Analytics and Artificial Intelligence (AI): These tools can analyze large sets of data to provide insights and predictive analytics. AI can optimize supply chains by predicting demand, managing risk, and enhancing procurement strategies.
Overall, the integration and optimization of these tools lead to enhanced efficiency, reduced costs, and improved customer satisfaction.
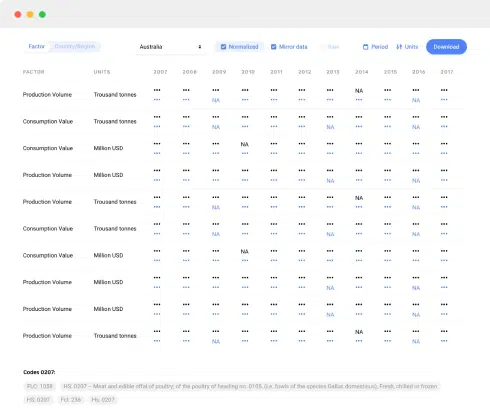
Nothing found. Please try again.
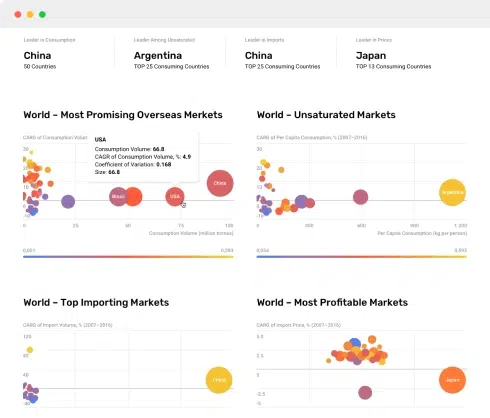
Nothing found. Please try again.
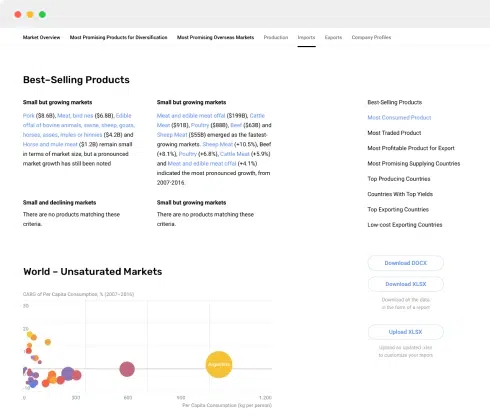
Nothing found. Please try again.